Important: Linux Experimental Version - I am making Regolith available to Linux as a desktop application. This is experimental at this time. If you encounter any error running this application in Linux please do let me know so I can resolve it - Thank you!
Regolith is a convenient app that approximates several calculations for the position, visibility, phases, eclipses, rising and setting times and other data about the moon. The program is not meant to be an exact representation of all the physics and mechanics that govern the moon; instead, Regolith is an aid to any observer, to quickly look up important data about the moon in a sufficiently accurate manner.
"Sufficiently Accurate" is a direct reference to Jean Meeus. This program was written as an implementation of Astronomical Algorithms, originally developed by Jean Meeus: his incredible work in the field of Computational Astronomy has been the inspiration for many works, including this one. While the calculations performed by Regolith are not meant to emulate NASA's ephemerides, Meeus' algorithms provide sufficient accuracy for the casual observer and amateur astronomer and that is what you will find here.
These are the functions that Regolith can perform:
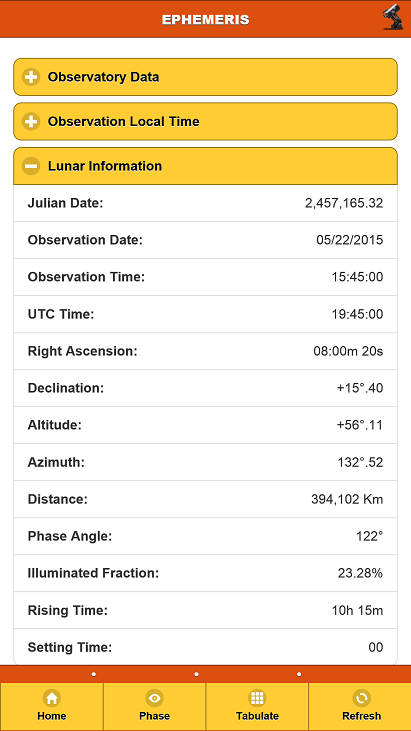
* Detailed ephemeris of the moon for a given date and time, including observer's coordinate and time location and altitude
* Visualization of the phases of the moon in a calendar-like format with real pictures obtained from NASA's LRO site
* Real-time almanac for any given month (from the years 2000 to 2050) including illuminated fractions
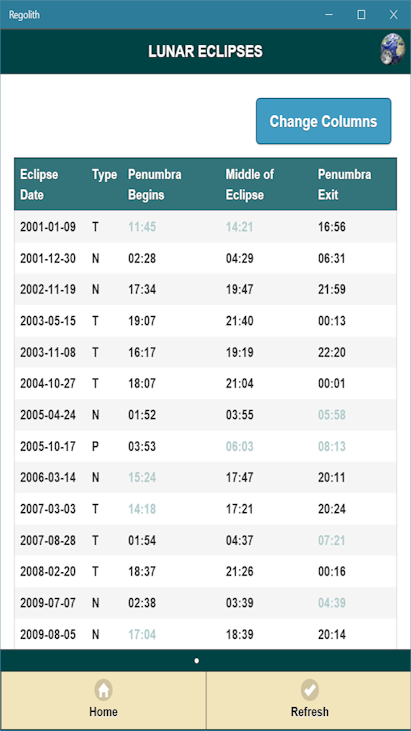
* A century of lunar eclipses, partial, total and penumbral
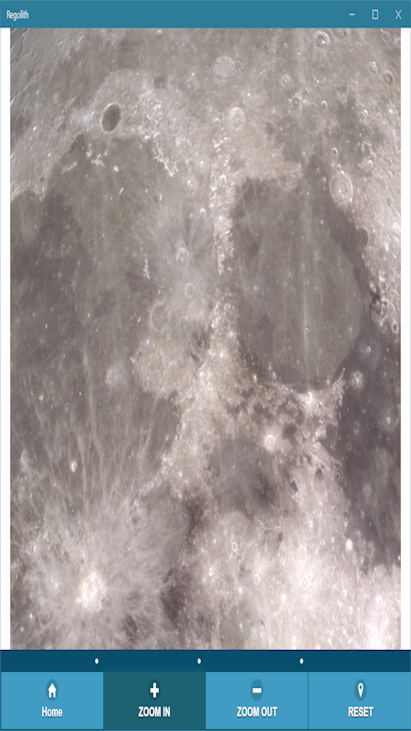
* A high resolution full moon for panning, scrolling and zooming into features as an observing aid
* Angle and date calculations to help you resolve your location and timing
* All calculations can be scrolled into the past or the future
* All screens link to each other for convenience
To use Regolith you must first establish your location profile (otherwise, all calculations default to midnight - Greenwich) - this is called your "observatory". You may look up your city's coordinated easily by searching google (for instance, "Washington DC coordinates" and simply enter the location angles provided in decimal form (e.g. 53.2366). Also check the box for Daylight Savings Time and enter your time offset from GMT (for instance, in the eastern US this would be 5 hours - no sign needed for positive offsets, use negative sign for negative offsets).
After your profile is set, time of day is controlled by the Ephemeris function thus, if you need to perform a calculation for a specific time, go to the Ephemeris page and change the time there. Upon entering this page the clock is always reset to the exact time on your device, for convenience.
Although we did not include a chart, the Ephemeris page will provide you information about altitude and azimuth for the moon as well as other positional data to help you locate it.